World’s oldest continually monitored rabbit site
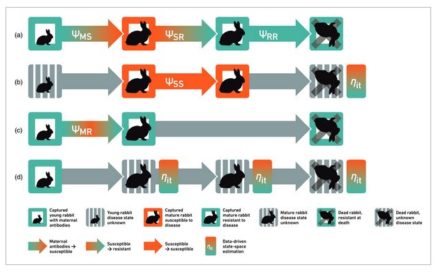
Monitored since an introduction of calicvirus in 1996, a rabbit colony on Turretfield Research Centre (South Australia) is the longest serving, continually monitored rabbit research site in the world. Data from the site have helped deliver a better understanding of rabbit biology, the transmission and effect of bio-controls (RHDV, RHDV2 and myxomatosis), and rabbit genetics, […]